Hi everyone, today I will talk about the Pineapple device and its installation as much as I can. I’m thinking of writing about this topic in parts. Today, I will be talking about what this device does and how to install it.
A Pineapple device, also known as a Wi-Fi Pineapple, is a tool used for targeting and compromising wireless communication networks. It derives its name from the resemblance its antennas bear to the spikes on a pineapple’s outer skin. The Pineapple device is often employed by individuals with malicious intent to exploit vulnerabilities in Wi-Fi networks.
What Inside a Pineapple Device Box?
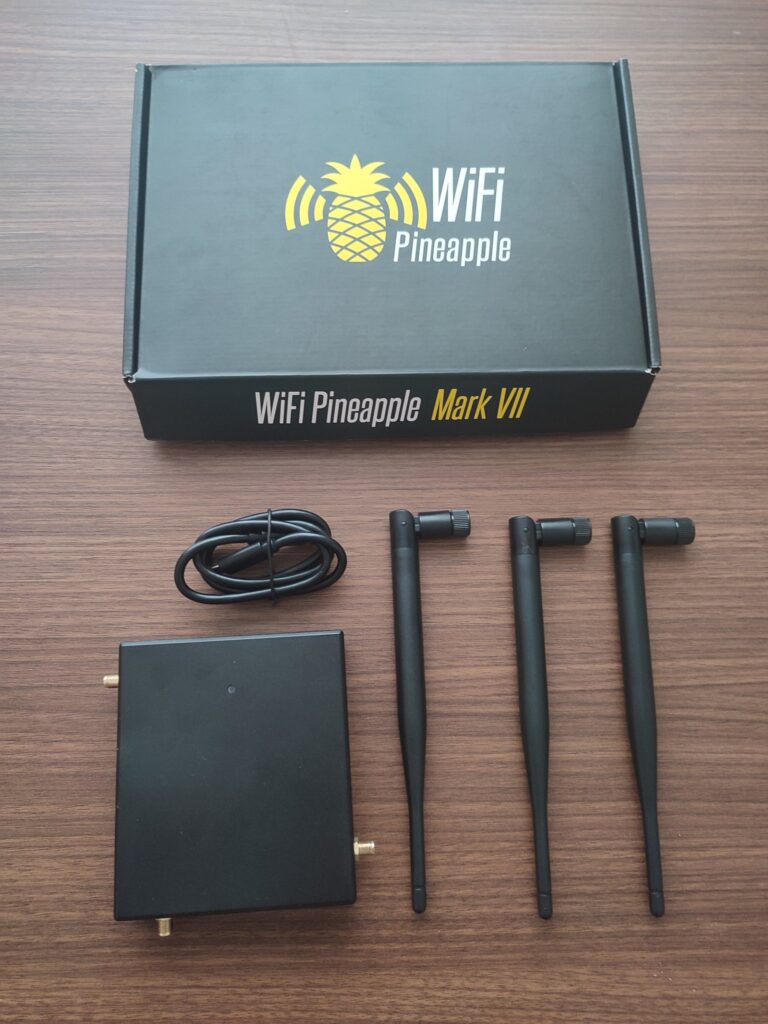
When you open a Pineapple device box, you’ll typically find the following components:
Pineapple Device: The core component of the package is the Pineapple device itself, which is a small, portable, and often inconspicuous hardware tool designed for conducting various wireless network security tests and assessments.
Power Adapter: A power adapter is usually included to provide the Pineapple device with the necessary electrical power. This adapter connects to the Pineapple device via a power input port.
Antennas: Pineapple devices often come with removable antennas. These antennas can be attached to the device to improve wireless signal reception and transmission, increasing the device’s effectiveness.
Ethernet Cable: An Ethernet cable is included to connect the Pineapple device to a computer or router for configuration and management. This is useful for setting up the device and performing certain functions.
Quick Start Guide: A quick start guide provides basic instructions on how to get the Pineapple device up and running. It typically includes information on connecting to the device, configuring it, and performing initial setup.
Accessories: Depending on the manufacturer and model, you may also find additional accessories or cables for specific use cases. These can include USB cables, additional power options, and carrying cases.
Authentication and License Information: Some Pineapple devices come with authentication or licensing information required to access advanced features or updates for the device’s firmware and software.
It’s important to note that the exact contents of a Pineapple device package may vary depending on the manufacturer, model, and version of the device. Users should refer to the specific product documentation provided with their Pineapple device for precise information regarding the package contents and setup instructions.
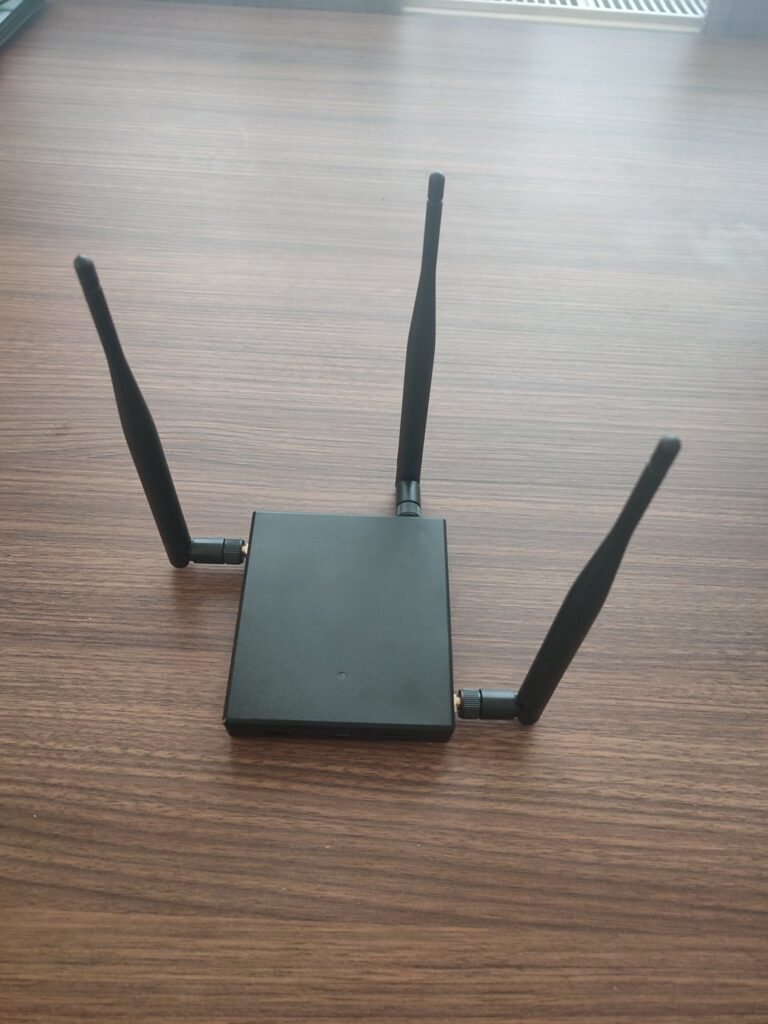


How to Install?
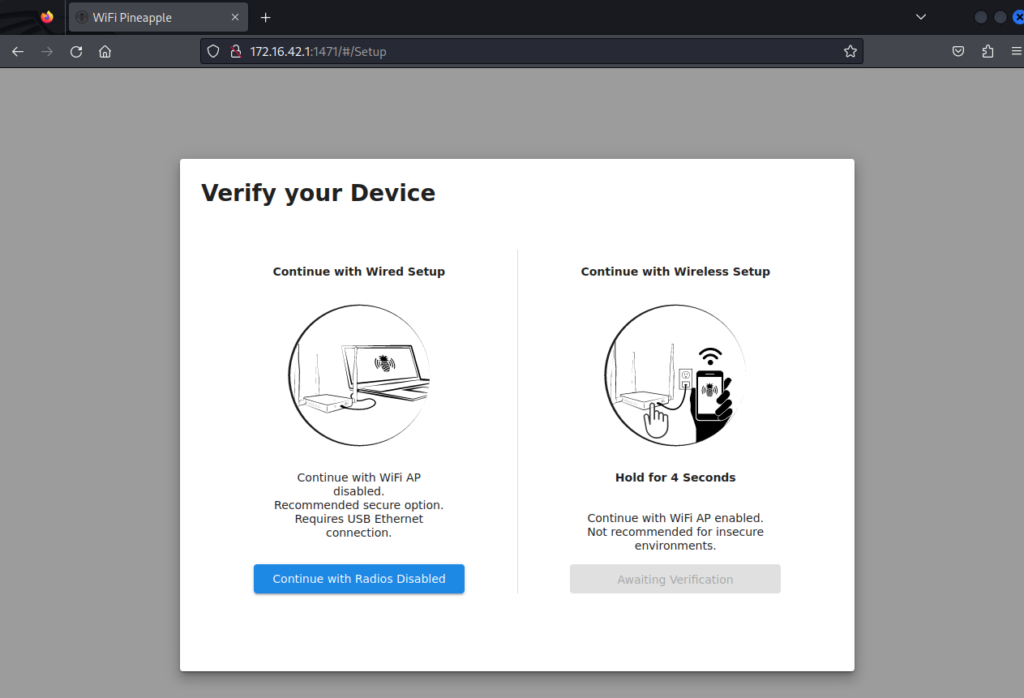
The device is connected to the computer via Type C input. After the connection is made, go to http://172.16.41.1:1471 using the browser via Kali. There are two ways to install. Let’s continue with the “Wired Setup” option. Let’s click Continue with Radios Disabled and move on to the next step.
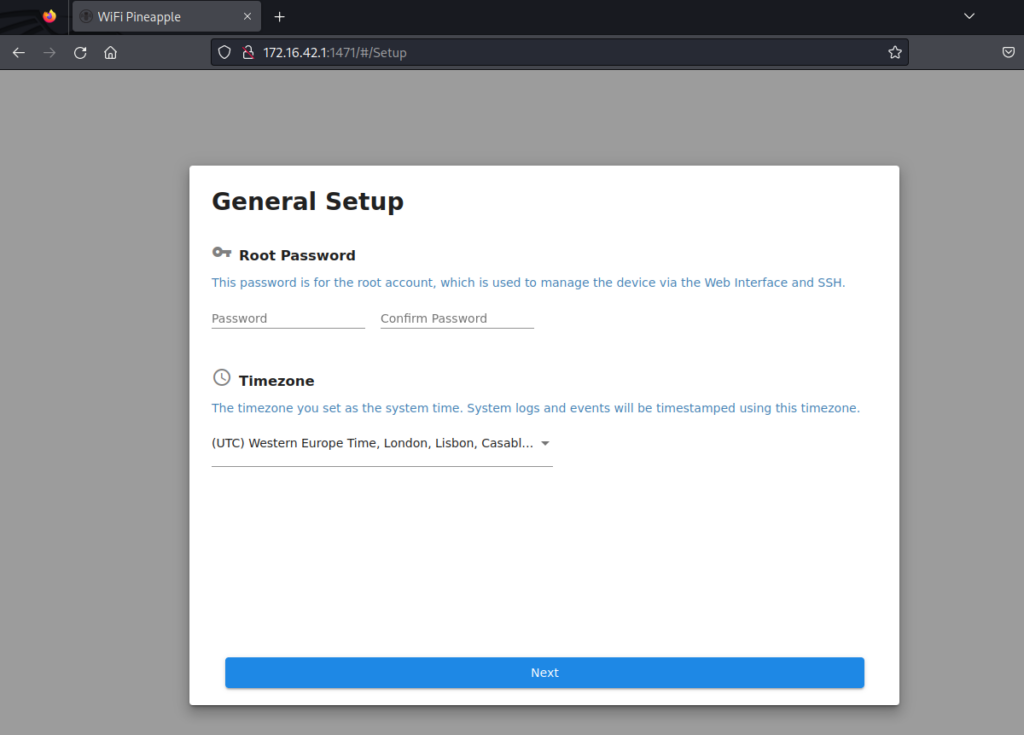
In this step, let’s set the root password. Remember the root password or you may have to reset the device.
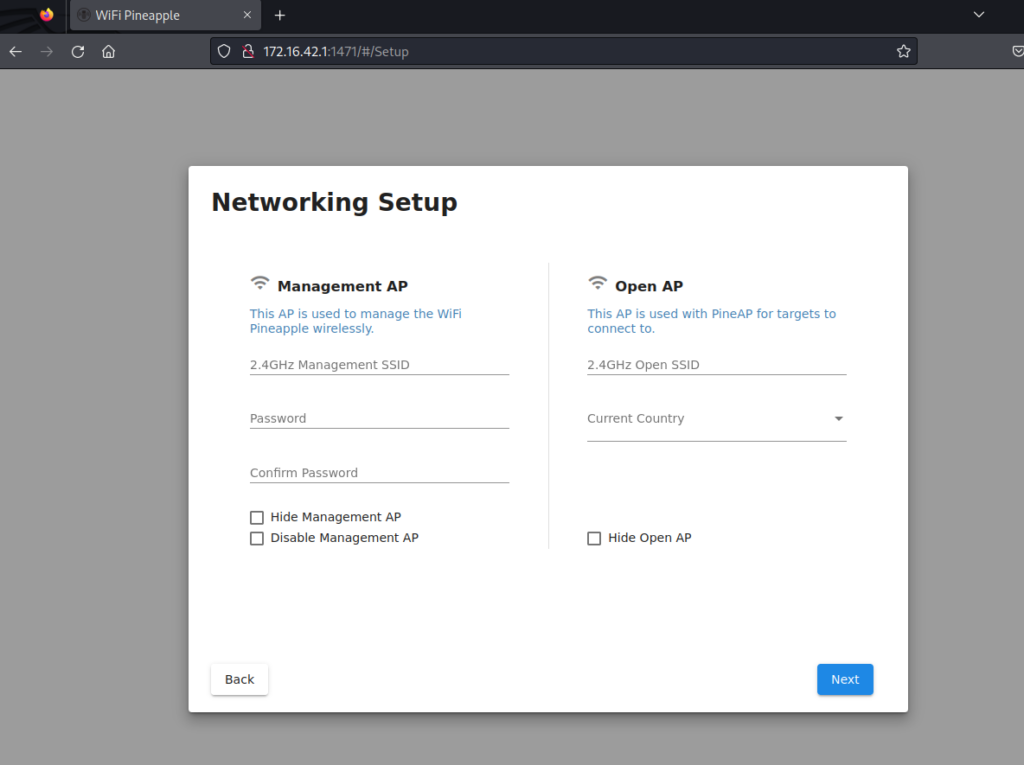
In this step, a management network name and password must be entered in the section on the left (Management AP). You can connect and manage it here. The open free network name (Open AP) is entered in the section on the right. This free network name is the name of the network that will be fake broadcast to the outside. If you select the “Hide Management AP” or “Hide Open AP” options, the relevant networks will be hidden.
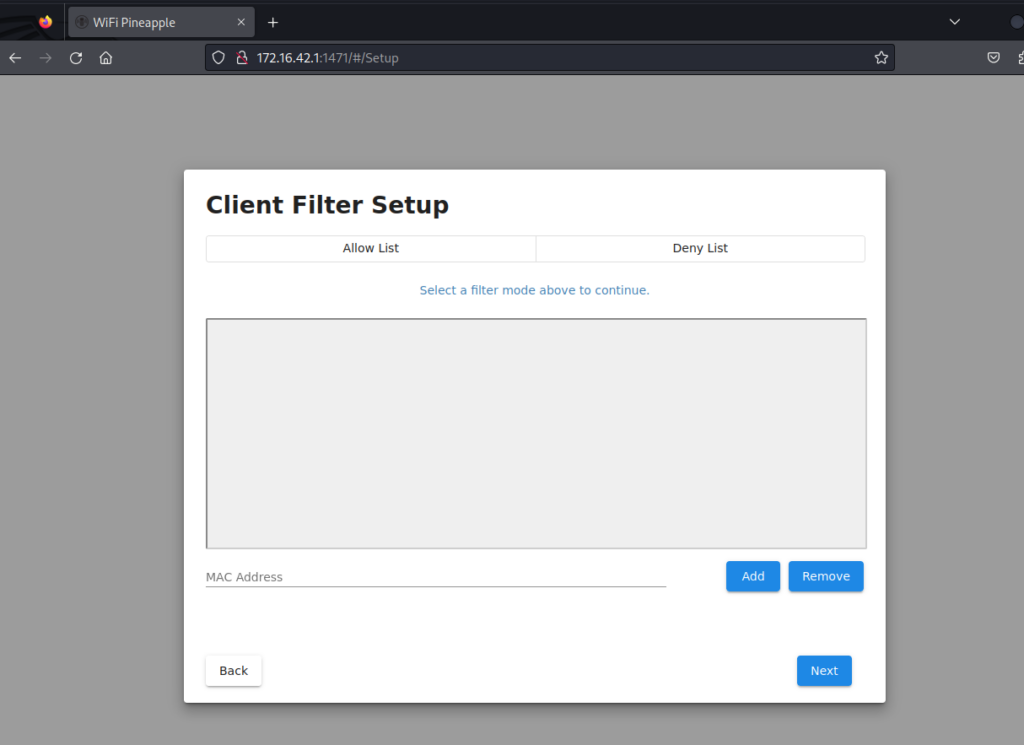
If there is a filtering for MAC addresses, it can be done here. Let’s leave this blank for now.
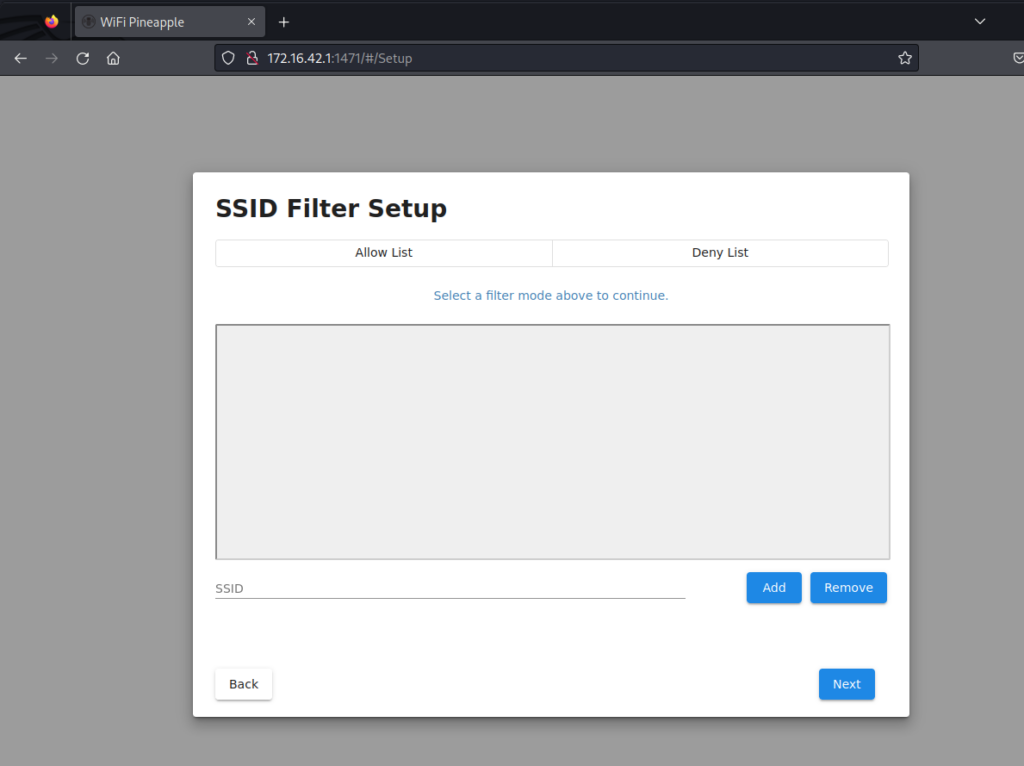
If there is a filtering for SSID, it can be done here. Let’s leave this blank for now.
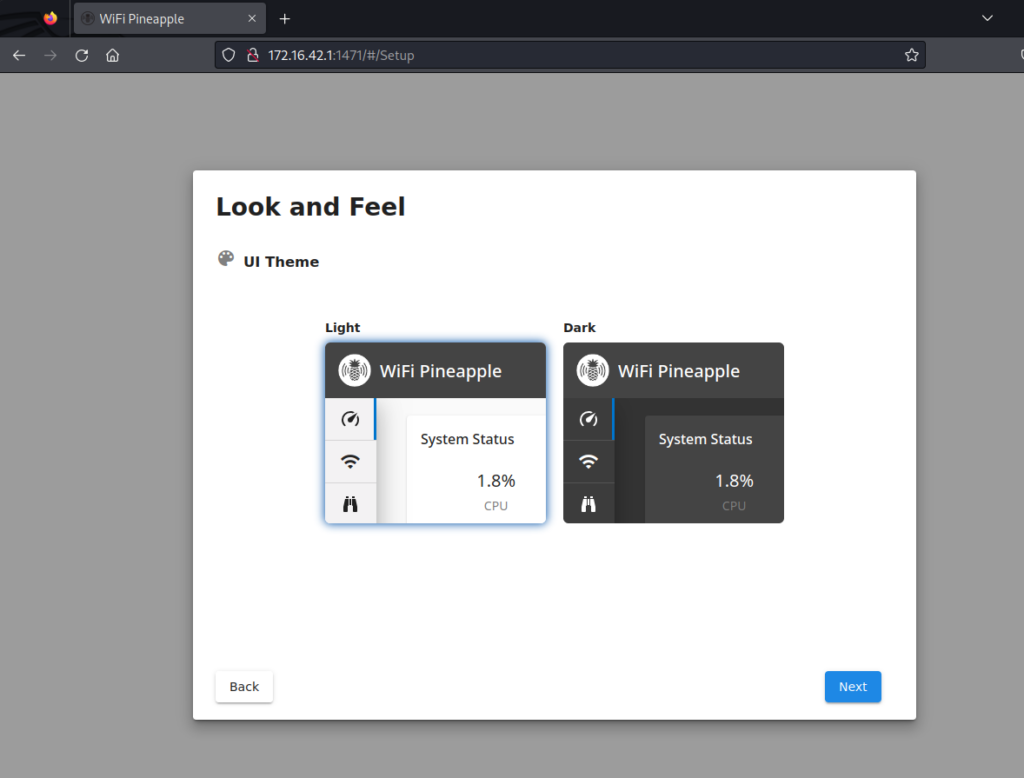
In this step, let’s choose our theme.
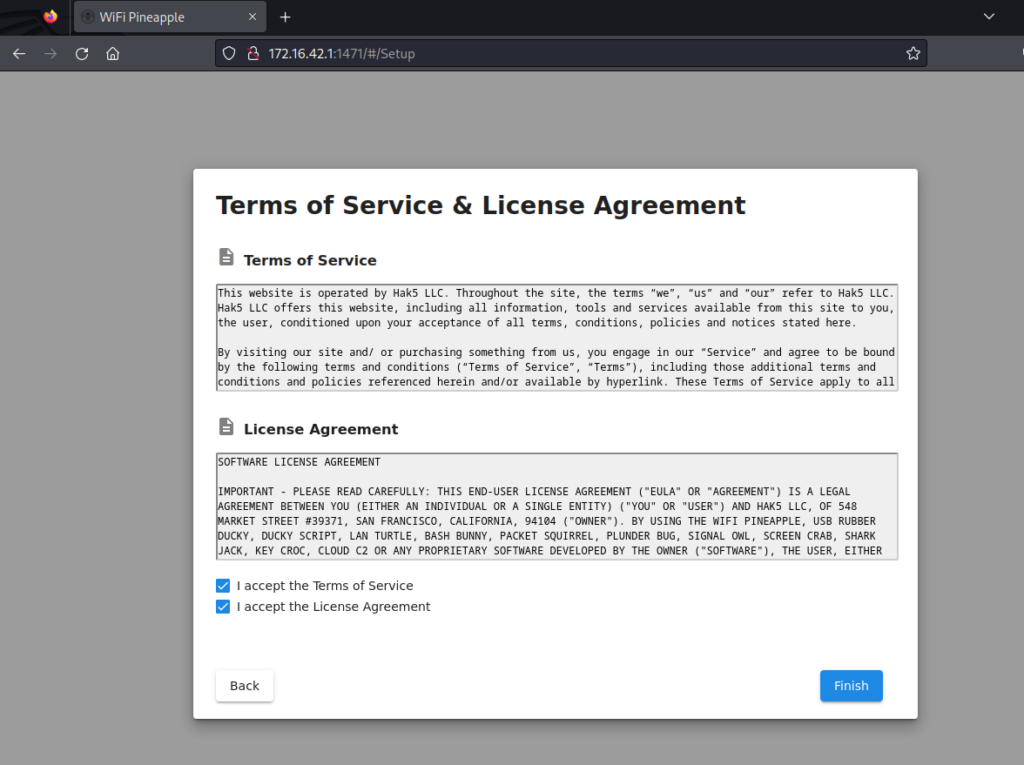
Let’s accept the license and agreement and complete the installation process by clicking Finish.
How Attacks Can Be Conducted Using a Pineapple Device
Pineapple devices, while having legitimate applications for network testing and security assessments, can also be misused for malicious purposes. Some of the common attack methods using a Pineapple device include:
- Karma Attack: The Pineapple can conduct Karma attacks by responding to probe requests from client devices searching for known networks. It sets up rogue access points that mimic familiar Wi-Fi networks, tricking users into connecting to them. This attack can intercept data and credentials sent over these fake networks.
- Evil Twin (Phishing) Attack: Pineapple devices can be configured to create Evil Twin access points that impersonate legitimate networks. Users connecting to these fake networks may unknowingly provide login credentials, which are then captured by the attacker through a spoofed login page.
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks: Pineapple devices can send deauthentication frames to clients, causing them to disconnect from a network. This disruption can lead to service outages and network instability.
- Phishing (Man-in-the-Middle Attacks): Pineapple devices can perform man-in-the-middle attacks by intercepting network traffic and redirecting it through the device. This enables the capture of sensitive data, such as login credentials and personal information.
It’s important to highlight that deploying Pineapple devices for malicious purposes is illegal and unethical. Unauthorized penetration testing and network assessments can result in criminal charges and severe legal consequences. Ethical use of these devices is paramount, and they should only be employed with proper authorization and within the boundaries of the law. Users should prioritize responsible and lawful usage and remain vigilant about the potential risks and security implications associated with Pineapple devices.
In our next article, we will examine what attacks can be carried out using Pineapple and how we can take precautions against these attacks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Pineapple device package typically includes essential components such as the Pineapple device itself, power adapter, antennas, Ethernet cable, quick start guide, and sometimes additional accessories. These devices serve a wide range of legitimate purposes, including network security testing and assessments. However, it is crucial to emphasize that the responsible and lawful use of Pineapple devices is paramount. Unauthorized or unethical use can result in legal consequences and breaches of ethical standards. Users should always adhere to applicable laws and ethical guidelines while using Pineapple devices, and they should obtain proper authorization before conducting any security assessments or tests. Furthermore, staying informed about the capabilities and potential risks associated with such tools is essential for using them in a responsible and constructive manner.
